Gas Water Heater: Reliability and Efficiency
Water heaters are an integral part of our daily lives, providing us with hot water for various household needs. Among various types of water heaters, one of the most common and efficient options is the gas water heater. In this article, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of gas water heaters, their operating principle, and popular models.
Operating Principle of a Gas Water Heater
A gas water heater is a device that utilizes natural gas or propane to heat water. The primary component of a gas water heater is the burner, which ignites the gas and transfers heat to the water in a specialized tank. Water is supplied to the tank, where it is heated and stored until it is needed. When you open a hot water faucet, hot water flows into your taps and showers.
Advantages of Gas Water Heaters
- Fast Heating: Gas water heaters typically heat water much faster than electric water heaters. This is especially important when you need hot water suddenly.
- Cost Efficiency: Natural gas is often less expensive than electricity, allowing you to save on energy bills.
- High Performance: Gas water heaters can provide a large volume of hot water, making them particularly useful for households with numerous members.
- Durability: Gas water heaters generally have a longer service life compared to their electric counterparts due to the absence of wear-prone electronic components.
Disadvantages of Gas Water Heaters
- Need for Gas Access: If you lack access to natural gas, using a gas water heater becomes problematic.
- Gas Emissions: Gas water heaters release combustion byproducts into the atmosphere, which may require special ventilation systems and have an adverse environmental impact.
- Installation: Installing a gas water heater may require professional services to ensure safety and efficiency.
Components of Gas Water Heater:
Tank: This is the container where water is stored until it’s needed. The tank can be made from various materials, such as steel, stainless steel, or fiberglass. The internal lining of the tank prevents corrosion.

Burner: A gas water heater is equipped with a burner that burns natural gas (or propane) to heat the water. The burner is typically located below the tank and ignites the gas using a piezoelectric ignition or an electric spark.

Gas Line: This is a pipeline that delivers natural gas from the source (gas line) to the gas valve of the water heater.
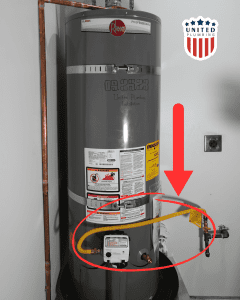
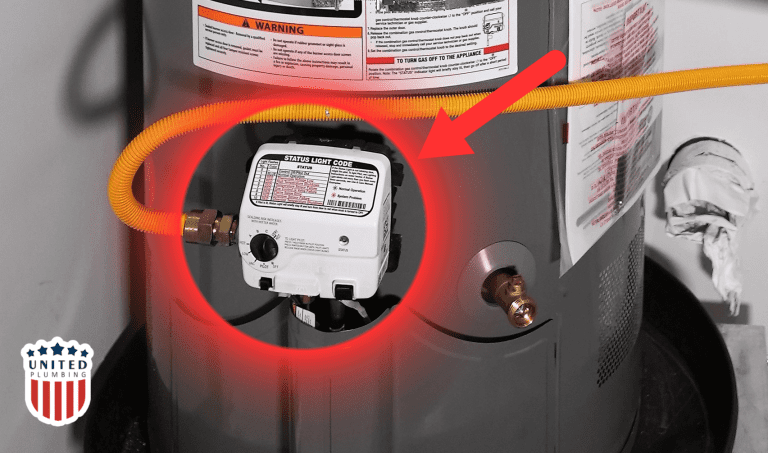
Gas Control Valve: is a critical component responsible for regulating the flow of natural gas or propane to the appliance’s burner. Its primary function is to control the supply of fuel, which in turn affects the heating process and ultimately the temperature of the water in the case of a water heater.
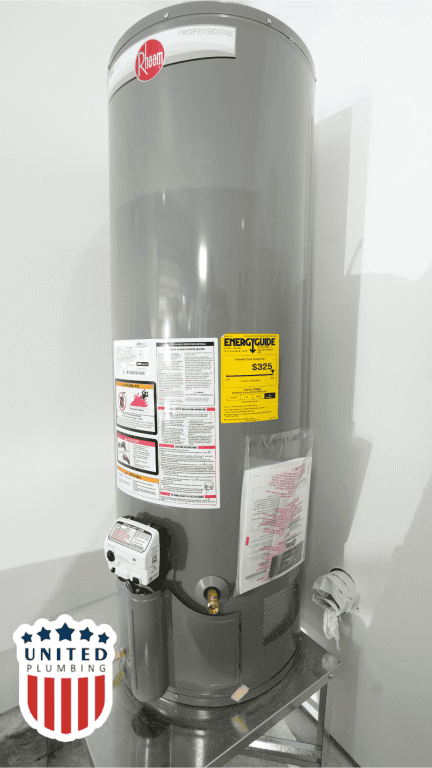
Anode Rod: The anode rod is designed to protect the tank from corrosion. It attracts corrosive elements, extending the tank’s lifespan.

Nipples: Water heater nipples are small, often overlooked components that play a crucial role in connecting water pipes to a water heater. These short pieces of pipe, typically made of brass, steel, or other durable materials, serve as connectors between the plumbing system and the water heater tank.

Flue and Exhaust Pipe: The flue and exhaust pipe are used to vent combustion byproducts from the water heater into the surrounding environment. This is essential for ensuring safety and the heater’s efficiency.
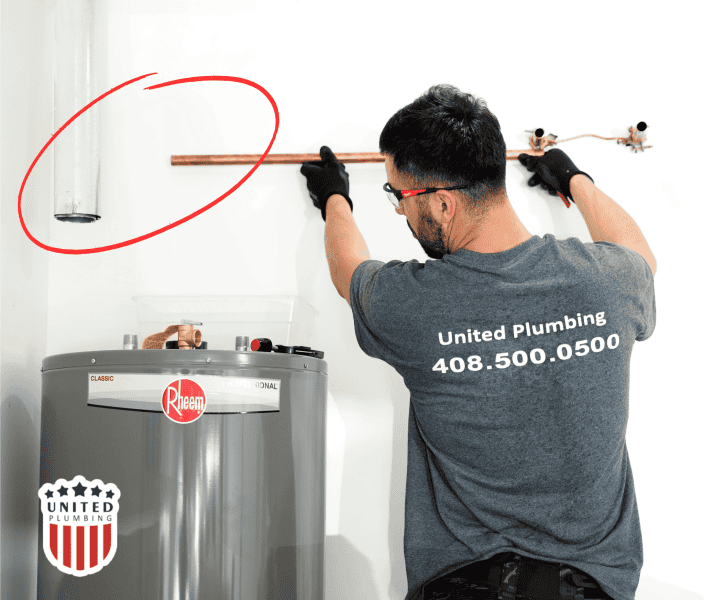

In conclusion, gas water heaters are an excellent solution for providing hot water to your home. They offer high performance, reliability, and cost efficiency, but they require access to natural gas and special safety measures. The choice of the appropriate model depends on your needs, budget, and available resources.
Post views: 635