What causes sediment buildup in the water heater?
However, over time, sediment buildup in water heaters can lead to decreased efficiency, increased energy consumption, and even potential damage to the appliance. Understanding the causes of sediment in water heaters and implementing preventive measures, especially in areas with hard water, can extend the lifespan of your water heater and improve its performance.
Causes of Sediment in Water Heaters
Sediment accumulation in water heaters is often linked to the presence of hard water. Hard water contains high levels of minerals, primarily calcium and magnesium ions. When hard water is heated, these minerals tend to precipitate and settle at the bottom of the water heater tank, forming a layer of sediment. Over time, this sediment can build up, creating a barrier between the heating element and the water, reducing the heater’s efficiency.
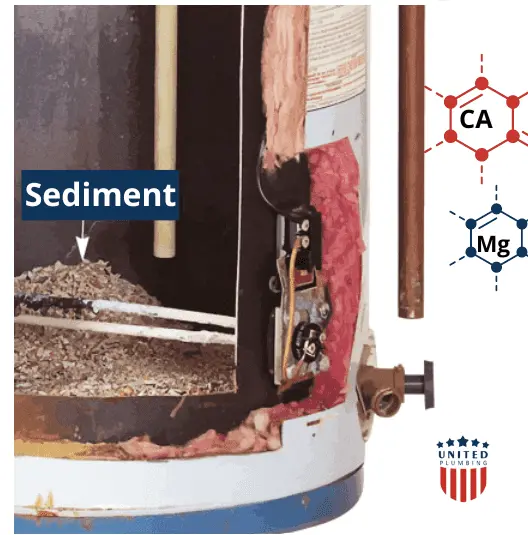
In addition to hard water, sediment can also result from the natural corrosion of the tank’s inner lining, rust particles, and debris carried by the incoming water supply. This accumulation not only diminishes the efficiency of the water heater but can also lead to overheating, increased energy consumption, and a shorter lifespan for the appliance. You can read more about corrosion here.

DIY Test for Hard Water:
Water hardness testing strips, also known as water hardness test kits, provide a more precise measurement of the mineral content in water. These strips are readily available at hardware stores, home improvement centers, or online, and they offer a convenient way to assess water hardness levels. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to conduct a water hardness test using testing strips:
Materials Needed:
- Water hardness testing strips
- Clear container or glass
- Water sample (representative of the source you want to test)
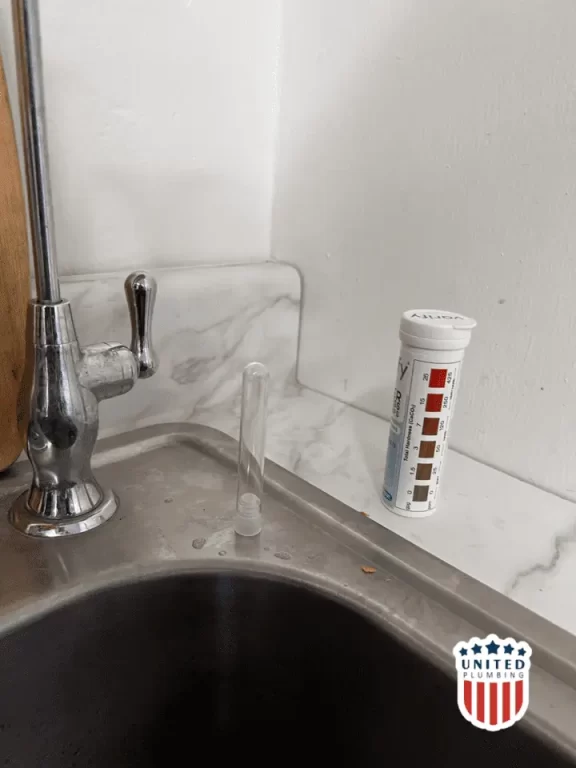

Procedure:
1. Collect a Water Sample:
Start by collecting a sample of the water you want to test. Ensure that the container used is clean and free from any contaminants that could affect the test results.
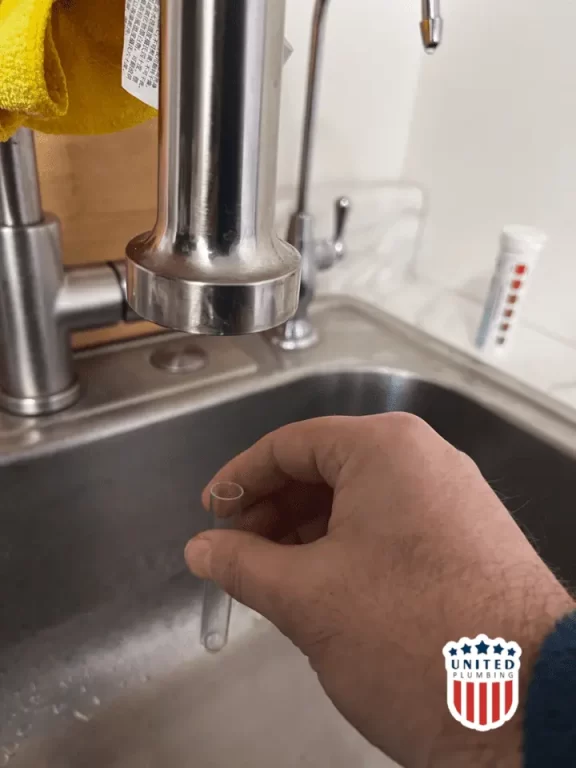

2. Dip the Testing Strip:
Take one water hardness testing strip and dip it into the water sample for a few seconds. Make sure the entire reactive area of the strip is submerged to obtain an accurate reading.
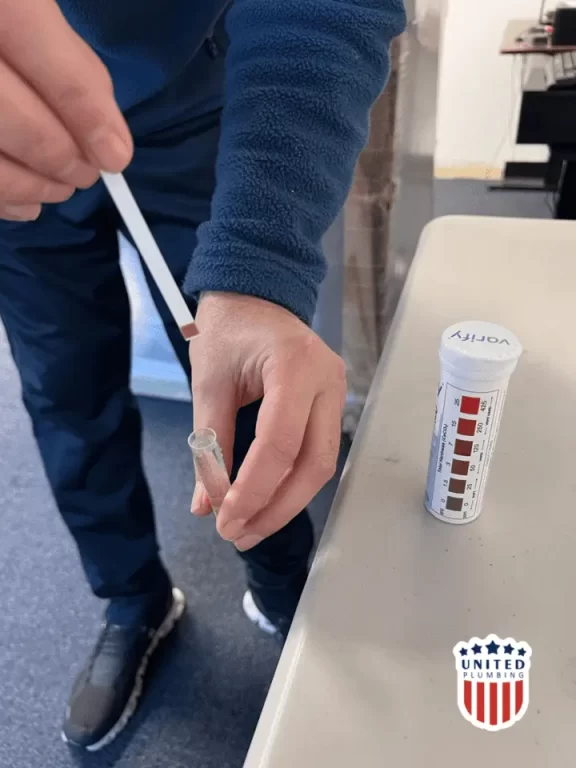

3. Remove Excess Water:
After dipping, gently shake the strip to remove excess water. Be cautious not to wipe or touch the reactive area, as this could interfere with the results.
4. Wait for Color Development:
Allow the testing strip to sit undisturbed for the recommended time specified by the manufacturer. Typically, this is around 1-2 minutes.
Compare Colors:
Once the waiting period is over, compare the color of the reactive area on the strip to the color chart provided with the testing kit. The chart will indicate the corresponding level of water hardness in terms of parts per million (ppm) or grains per gallon (gpg).
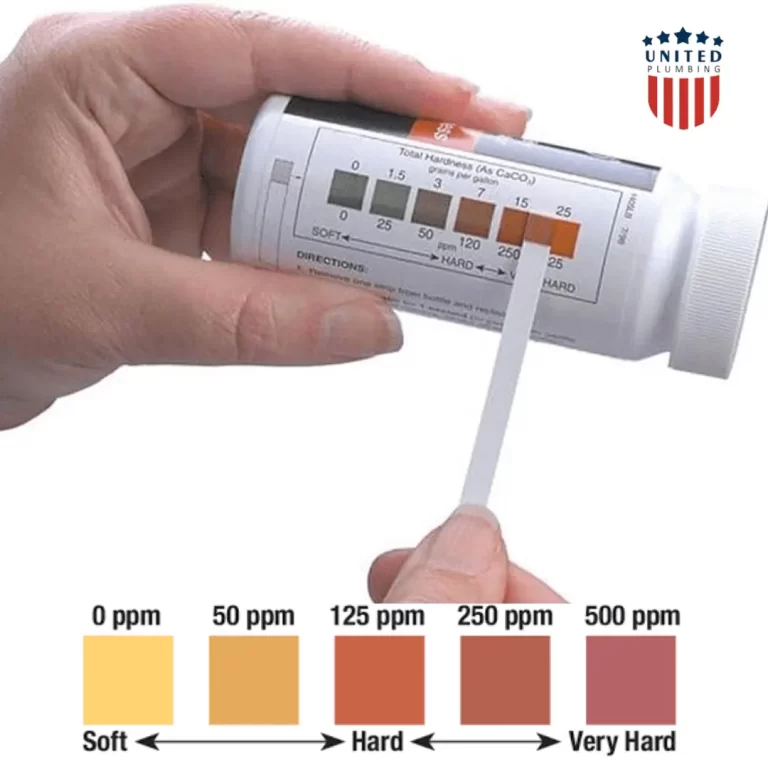
Soft Water: Light colors on the strip (e.g., green, yellow or blue) indicate low mineral content.
Moderate Hardness: The strip may turn to shades of yellow.
Hard Water: Darker colors, such as orange or red or brown, suggest high mineral content.
Record the Results:
Note the color match and refer to the water hardness scale provided. Record the hardness level for future reference.
In conclusion, sediment buildup in water heaters is a common issue that can be attributed to factors such as hard water, corrosion, and debris in the water supply. Taking proactive steps to address these causes is essential for maintaining the efficiency and lifespan of your water heater.
If hard water is identified as the culprit behind sediment accumulation, consider installing a water softener, read more here. These devices are designed to mitigate the impact of minerals like calcium and magnesium, preventing them from settling in the tank and causing issues. Regular flushing, sediment filters, and adjusting the water heater temperature are additional measures that can contribute to a sediment-free and efficient system.
However, if corrosion is identified as the root cause of sediment in your water heater, it’s crucial to address the issue promptly. Corrosion can lead to serious damage and compromise the integrity of the tank. For urgent guidance on dealing with corrosion-related sediment, read here.
By staying informed and implementing preventive measures tailored to the specific cause of sediment buildup in your water heater, you can ensure a reliable and energy-efficient hot water supply for years to come. Regular maintenance and the right interventions will not only save you money on energy bills but also extend the life of your water heater, providing you with peace of mind and comfort.
Post views: 731